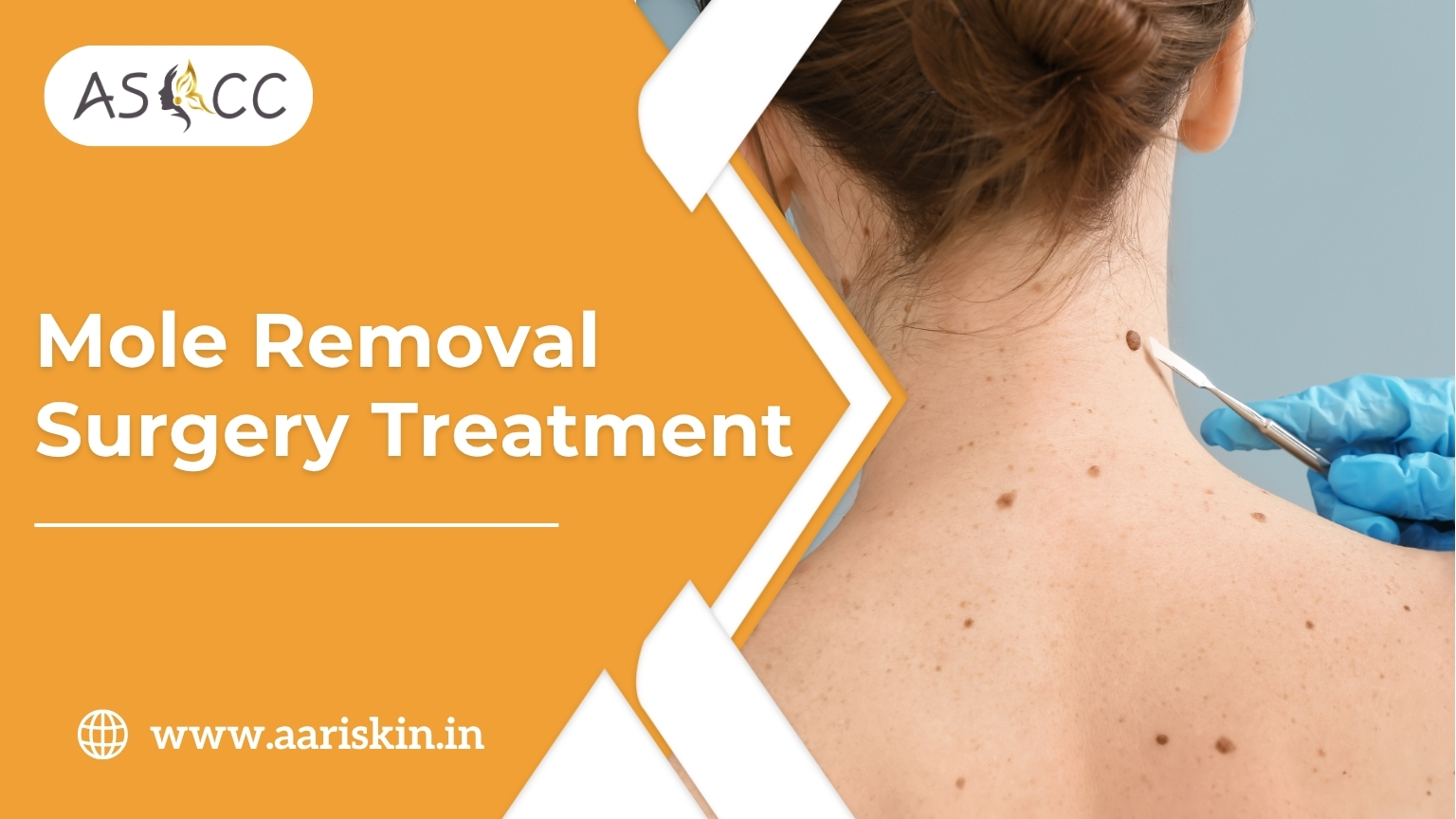
What is a Mole?
A mole (also called a nevus) is a small, pigmented spot or growth on the skin caused by clusters of melanocytes (pigment-producing cells). Moles are usually harmless, but some people choose to remove them for cosmetic reasons or if there’s concern about abnormal growth.
What is Mole Removal Surgery?
Mole removal surgery is a minor procedure to safely remove raised, flat, or suspicious moles from the skin using surgical or non-surgical techniques. It is done under local anesthesia and typically leaves minimal or no scarring when done by trained professionals.
Why Moles Are Removed:
| Medical Reasons | Cosmetic Reasons |
|---|---|
| Change in size, color, or shape | Visible or large mole on face or neck |
| Itching, bleeding, or pain | Multiple moles affecting appearance |
| Suspicion of skin cancer | Asymmetry or irregular shape |
Types of Mole Removal Techniques:
Surgical Excision
- The mole is cut out completely with a small margin of skin
- Stitches may be required
- Used for deep or large moles, or if cancer risk is suspected
- Sent for biopsy (lab testing) if needed
Shave Excision
- The mole is shaved off flush with the skin
- No stitches needed
- Best for raised moles that are non-cancerous
Laser Mole Removal
- Uses focused laser energy to remove superficial pigmented moles
- Ideal for flat, small, or cosmetic moles
- No cutting, no stitches, very minimal scarring
🕒 Treatment Details:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Procedure Time | 15–30 minutes |
| Anesthesia | Local (numbing cream or injection) |
| Recovery Time | 5–10 days depending on method |
| Biopsy Required | Only for suspicious-looking moles |
| Pain Level | Minimal to none |
Who is it For?
- Anyone with a suspicious or irritating mole
- People seeking cleaner skin appearance (face, neck, hands)
- Patients referred by dermatologists or cosmetic surgeons
Aftercare Tips:
- Keep the area clean and dry
- Use prescribed healing ointment or antibiotic cream
- Avoid sun exposure until fully healed
- Do not scratch or rub the treated area
- Follow-up if stitches are used or biopsy is done
Not Suitable For:
- Active infections at the treatment site
- Uncontrolled bleeding/clotting disorders (doctor will evaluate)
- Very large or deep moles may require layered surgical planning